On November 16, 1965, the automatic interplanetary station 3MV-3 No. 1, weighing 960 kg, known as Venera-3, was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the USSR.
The unmanned spacecraft Venera-3 became the first messenger from Earth to land on the surface of another planet – Venus.
The unmanned spacecraft Venera-3 became the first messenger from Earth to land on the surface of another planet – Venus.
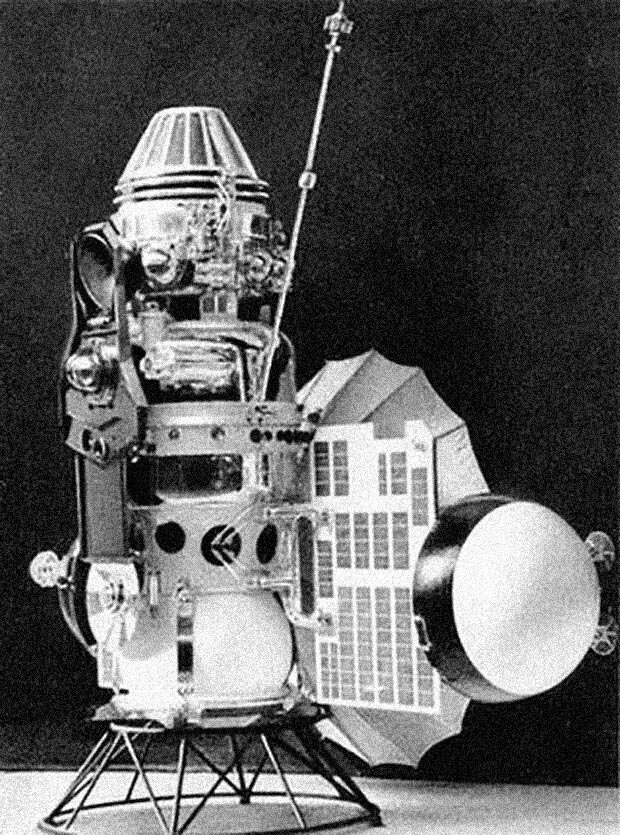
The exploration of Venus began under the initiative of Sergei Pavlovich Korolev, who in 1950 was appointed as the chief designer of the Special Design Bureau No. 1 (OKB-1), which is now known as S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation "Energia". It was at OKB-1 that the Venera-3 spacecraft was developed and manufactured.
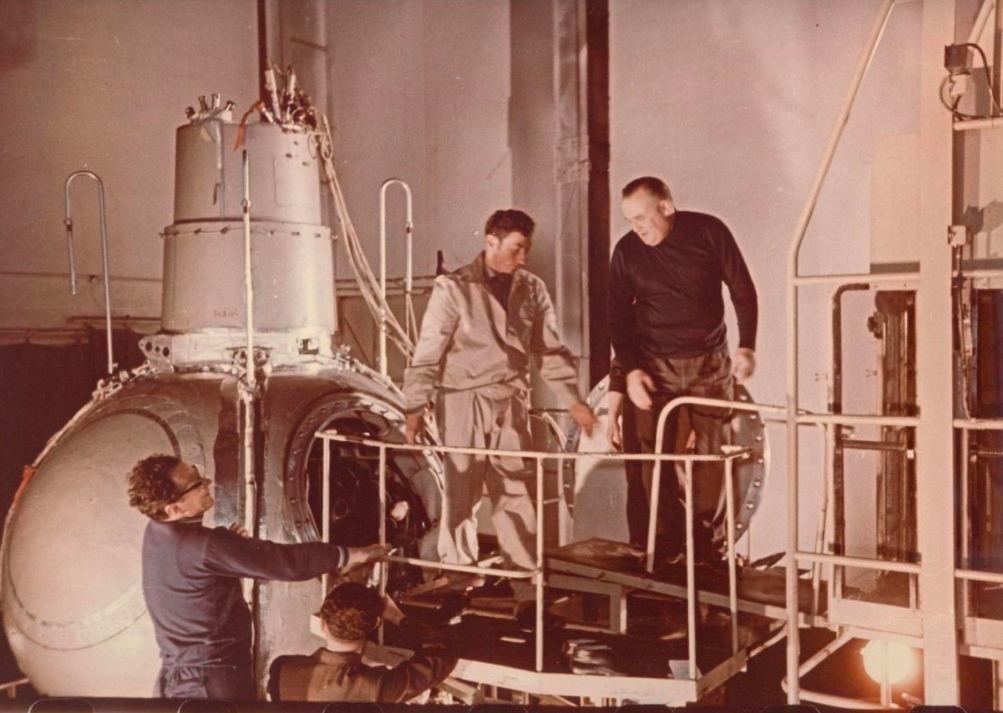
S.P. Korolev in the assembly shop, early 1960s. From the collections of the Cosmonautics Museum.
Venera-3 reached the surface of Venus on March 1, 1966. The mission took place against a backdrop of uncertainty regarding the conditions on Venus, which is hidden beneath several kilometers of cloud cover. The descent module encountered conditions that were much harsher than scientists had anticipated: the temperature and atmospheric pressure on Venus turned out to be incredibly high, leading to the failure of the spacecraft.
Although Venera-3 was unable to transmit data about the planet itself, significant scientific information was gathered during its flight. This data contributed to a deeper understanding of magnetic fields, low-energy charged particle flows, solar plasma and its energetic characteristics, as well as cosmic radio emissions. The information obtained from trajectory measurements became a valuable resource for further studies related to deep-space communication and interplanetary travel.
Although Venera-3 was unable to transmit data about the planet itself, significant scientific information was gathered during its flight. This data contributed to a deeper understanding of magnetic fields, low-energy charged particle flows, solar plasma and its energetic characteristics, as well as cosmic radio emissions. The information obtained from trajectory measurements became a valuable resource for further studies related to deep-space communication and interplanetary travel.

